Overview
Cataracts is the name given to the natural lens inside the eye when it has become cloudy or less clear in appearance. When cloudy patches appear in your vision, it stops the light from reaching the back of your eyes which causes the impaired vision. A common misconception is that the cataract is like a “film” or “skin” that has grown over the eye, and this simply is not true. In actual fact, if you are suffering from a cataract, then the lens itself has gone cloudy and this can occur due to age, trauma, diabetes, or genetics to name a few causes.
Cataracts are very common; it’s estimated around 2.5 million people aged over 65 have cataracts and it’s the main cause of impaired vision worldwide. Most cataract cases develop over time, some patients may not even notice they have cataracts until it eventually disturbs their vision. In early cases, stronger glasses can help with developing cataracts but it will not stop the development but surgery is most beneficial in the early stages.
Signs and symptoms of Cataracts:
- You may have clouded, blurred or dim vision
- Increasing difficulty with vision at night
- Heightened sensitivity to light and glare
- Seeing "halos" around lights
- Frequent changes in eyeglass or contact lens prescription
- Fading or yellowing of colours
- Double vision in a single eye
Causes
There can be a number of causes for cataracts and they can simply occur from ageing and the changes of tissue that makes your eye’s lens. People who are 65 and over are more prone to developing cataracts. Other possible causes may be:
- Smoking
- Poor diet
- Alcohol abuse
- Drug and steroid medication use
- Health conditions such as diabetes
- A family history of cataracts
- Exposure to UV lights throughout life
Diagnosis:
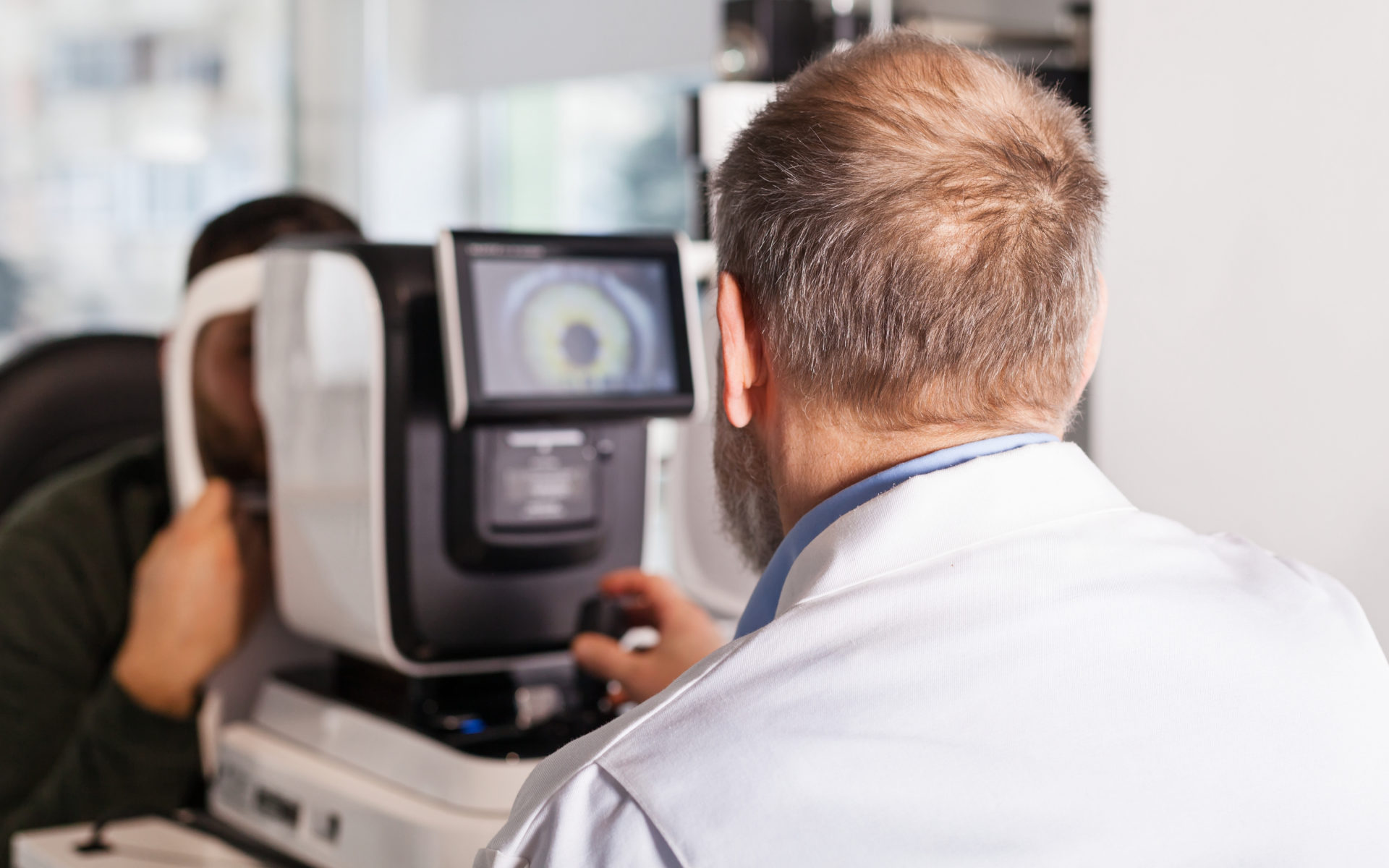
To diagnose cataracts a visual acuity test which is an eye exam that checks and measures how well you can read letters from a chart. It can measure how you discern shapes and can will be able to determine if your eyes are showing any signs of impairment.
A slit lamp exam is another way to diagnose cataracts. It is a high-intensity light where they microscopically examine different views of your eyes including eyelids, conjunctiva, iris, lens, sclera and more.
Lastly, cataracts can be diagnosed through a retinal exam where drops are placed in your eyes to dilate your pupils so the back of your eyes can be examined using a slit lamp.
If you would like to read more about the treatments we offer for cataracts, please click here
This article is intended to inform and give insight but not treat, diagnose or replace the advice of a doctor. Always seek medical advice with any questions regarding a medical condition.